
1. In Fig. 6.39, sides QP and RQ of ` \▵PQR\ ` are produced to points S and T respectively. If ∠SPR=135° and ∠PQT=110°, find ∠PRQ.
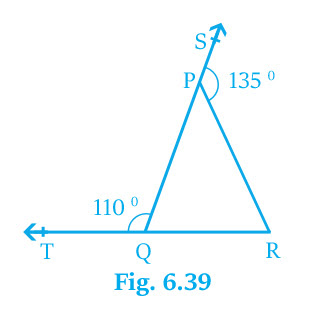
solution :
Given,
` \∠SPR=135°\ ` and ` \∠PQT=110°\ `
Find,
` \∠PRQ=?\ `
In the Fig,
Side QP and RQ of ` \▵PQR\ ` are produced to points S and T respectively.
` \∠SPR+∠QPR=180°\ `[ Linear pair of angels ]
` \=>135°+∠QPR=180°\ `` \[∴∠SPR=135°]\ `
` \=>∠QPR=180°-135°\ `
` \=>∠QPR=45°\ `
Similarly,
` \∠PQT+∠PQR=180°\ `[ Linear pair of angels ]
` \=>110°+∠PQR=180°\ `` \[∴∠PQT=110°]\ `
` \=>∠PQR=180°-110°\ `
` \=>∠PQR=70°\ `
Now,
In ` \▵PQR\ `,
` \∠PRQ+∠PQR+∠QPR=180°\ `[ Angle sum property of a traingle ]
` \=>∠PRQ+70°+45°=180°\ `[∴` \∠PQR=70°\ ` and ` \∠QPR=45°\ `]
` \=>∠PRQ+115°=180°\ `
` \=>∠PRQ=180°-115°\ `
` \=>∠PRQ=65°\ `
So,
The value of ` \∠PRQ\ ` is ` \65°\ `.
2. In Fig. 6.40, ∠X=62°, ∠XYZ=54°. If YO and ZO are the bisectirs of ∠XYZ and ∠XZY respectively of ` \▵XYZ\ `, find ∠OZY and ∠YOZ.

solution :
Given,
` \∠X=62°\ `, ` \∠XYZ=54°\ ` and
YO and ZO are the bisectors of ∠XYZ and ∠XZY respectively of ` \▵XYZ\ `.
Find,
` \∠OZY=?\ ` and ` \∠YOZ=?\ `
In ` \▵XYZ,\ `
` \∠X+∠XYZ+∠XZY=180°\ `[ Angle sum property of a traingle ]
` \=>62°+54°+∠XZY=180°\ `[∴` \∠X=62°\ ` and ` \∠XYZ=54°\ `]
` \=>116°+∠XZY=180°\ `
` \=>∠XZY=180°-116°\ `
` \=>∠XZY=64°\ `
Now,
` \∠OZY=\frac{1}{2}∠XZY\ `[Given]
` \=>∠OZY=\frac{1}{2}×64°\ `` \[∴∠XZY=64°]\ `
` \=>∠OZY=32°\ `
Then,
` \∠OYZ=\frac{1}{2}∠XYZ\ `[Given]
` \=>∠OYZ=\frac{1}{2}×54°\ `` \[∴∠XYZ=54°]\ `
` \=>∠OZY=27°\ `
Now,
In ` \▵OZY,\ `
` \∠OZY+∠ZYO+∠YOZ=180°\ `[ Angle sum property of a traingle ]
` \=>32°+27°+∠YOZ=180°\ `[∴` \∠OZY=32°\ ` and ` \∠ZYO=27°\ `]
` \=>59°+∠YOZ=180°\ `
` \=>∠YOZ=180°-59°\ `
` \=>YOZ=121°\ `
So,
The value of ` \∠OZY=27°\ ` and ` \∠YOZ=121°\ `.
3. In Fig. 6.41, if AB ` \||\ ` DE, ∠BAC=35° and ∠CDE=53°, find ∠DCE.

solution :
Given,
AB ` \||\ ` DE, ` \∠BAC=35°\ ` and ` \CDE=53°\ `.
Find,
` \∠DCE=?\ `
In the Fig,
` \∠BAC=∠CED\ `[Alternate interior angles ]
` \=>∠CED=35°\ `` \[∴∠BAC=35°]\ `
Now,
In ` \▵CDE\ `,
` \∠CDE+∠CED+∠DCE=180°\ `[ Angle sum property of a traingle ]
` \=>53°+35°+∠DCE=180°\ `[∴` \∠CDE=53°\ ` and ` \∠CED=35°\ `]
` \=>88°+∠DCE=180°\ `
` \=>∠DCE=180°-88°\ `
` \=>∠DCE=92°\ `
So,
The value of ` \∠DCE\ ` is ` \92°\ `.
4. In Fig. 6.42, if lines PQ and RS intersect at point T, such that ∠PRT=40°,∠RPT=95° and ∠TSQ=75°, find ∠SQT.

solution :
Given,
` \∠PRT=40°\ `, ` \∠RPT=95°\ ` and ` \∠TSQ=75°\ `
Find,
` \∠SQT=?\ `
In ` \▵PRT\ `,
` \∠PTR+∠TRP+∠RPT=180°\ `[ Angle sum property of a traingle ]
` \=>∠PTR+40°+95°=180°\ `[∴` \∠TRP=40°\ ` and ` \∠RPT=95°\ `]
` \=>PTR+135°=180°\ `
` \=>∠PTR=180°-135°\ `
` \=>PTR=45°\ `
In the Fig.
` \∠PTR=∠QTS\ `[ Vertically opposit angles ]
` \∠QTS=45°\ `` \[∴∠PTR=45°]\ `
Now,
In ` \▵QTS\ `,
` \∠SQT+∠TSQ+∠QTS=180°\ `[ Angle sum property of a traingle ]
` \=>∠SQT+75°+45°=180°\ `[∴` \∠TSQ=75°\ ` and ` \∠QTS=45°\ `]
` \=>∠SQT+120°=180°\ `
` \=>∠SQT=180°-120°\ `
` \=>∠SQT=60°\ `
So,
The value of ` \∠SQT\ ` is 60°.
5. In Fig. 6.43, if PQ` \⊥\ `PS, PQ ` \||\ ` SR, ∠SQR=28° and ∠QRT=65°, then find the value of ` \x\ ` and ` \y\ `.
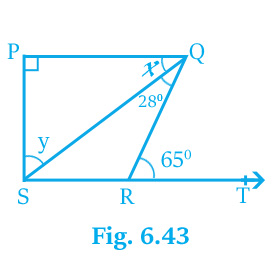
solution :
Given,
PQ` \⊥\ `PS, PQ ` \||\ ` SR, ` \∠SQR=28°\ ` and ` \∠QRT=65°\ `.
Find,
` \x=?\ ` and ` \y=?\ `
In the Fig.
` \∠QRS+∠QRT=180°\ `[ Linear pair of angels ]
` \=>∠QRS+65°=180°\ `` \[∴∠QRT=65°]\ `
` \=>∠QRS=180°-65°\ `
` \=>∠QRS=115°\ `
Now,
In ` \▵QRS\ `,
` \∠QSR+∠SQR+∠QRS=180°\ `[ Angle sum property of a traingle ]
` \=>∠QSR+28°+115°=180°\ `[∴` \∠SQR=28°\ ` and ` \∠QRS=115°\ `]
` \=>∠QSR+143°=180°\ `
` \=>∠QSR=180°-143°\ `
` \=>∠QSR=37°\ `
Then,
PQ ` \||\ ` SR and PS is transversal.
` \∠QPS+∠PSR=180°\ `[ Interior angles on the same side of the transversal ]
` \=>∠PSR+90°=180°\ `` \[∴∠QPS=90°]\ `
` \=>∠PSR=180°-90°\ `
` \=>∠PSR=90°\ `
` \=>∠PSR=∠PSQ+∠QSR\ `[ From Fig. ]
` \=>90°=y+37°\ `[ From Fig. and ` \∠QSR=37°\ ` ]
` \=>y=90°-37°\ `
` \=>y=53°\ `
Now,
In ` \▵PQS\ `,
` \∠QSP+∠SPQ+∠PQS=180°\ `[ Angle sum property of a traingle ]
` \=>53°+90°+∠PQS=180°\ `[∴` \∠QSP=53°\ ` and ` \∠SPQ=90°\ `]
` \=>143°+∠PQS=180°\ `
` \=>∠PQS=180°-143°\ `
` \=>∠PQS=37°\ `
` \=>x=37°\ `` \[∴∠PQS=x]\ `
So,
The value of ` \x\ ` is 37° and ` \y\ ` is 53°.
6. In Fig. 6.44, the side QR of ` \▵PQR\ ` is produced to a point S. If the bisectors of ∠PQR and ∠PRS meet at point T, then prove that ` \∠QTR=\frac{1}{2}∠QPR\ `.

solution :
Given,
` \∠PQR\ ` bisect QT and ` \∠PRS\ ` bisect RT.
Find,
` \∠QTR=\frac{1}{2}∠QPR\ `
In ` \▵PQR\ `,
` \∠PRS=∠QPR+∠PQR\ `[ Angle Sum Property of a Triangle ]
` \=>∠PRS-∠PQR=∠QPR\ `
` \=>∠QPR=∠PRS-∠PQR\ `` \----- (I)\ `
Similarly,
In ` \▵QTR\ `,
` \∠TRS=∠QTR+∠TQR\ `[ Angle Sum Property of a Triangle ]
` \=>∠TRS-∠TQR=∠QTR\ `
` \=>∠QTR=∠TRS-∠TQR\ `` \----- (II)\ `
Now,
` \∠PRS=∠PRT+∠TRS\ `[ From Fig. ]
` \=>∠PRS=∠TRS+∠TRS\ `[ From Fig. ` \∠PRT=∠TRS\ ` ]
` \=>∠PRS=2∠TRS\ `
` \=>∠TRS=\frac{1}{2}∠PRS\ `` \----- (III)\ `
Similarly,
` \∠PQR=∠PQT+∠TQR\ `[ From Fig. ]
` \=>∠PQR=∠TQR+∠TQR\ `[ From Fig. ` \∠PQT=∠TQR\ ` ]
` \=>∠PQR=2∠TQR\ `
` \=>∠TQR=\frac{1}{2}∠PQR\ `` \----- (IV)\ `
Now,
From (II), (III) and (IV).
` \∠QTR=\frac{1}{2}∠PRS-\frac{1}{2}∠PQR\ `
` \=>∠QTR=\frac{1}{2}(∠PRS-∠PQR)\ `` \----- (V)\ `
From (I) and (V).
` \=>∠QTR=\frac{1}{2}∠QPR\ `
Proved.




0 Comments